File History
To automatically back up your data files and to retrieve earlier versions of them, you are provided with a new type of backup program called Windows File History. To use File History, you'll need a second storage device, such as a USB hard drive or SD card, or you could use a network location, such as a shared folder on another PC on your network for the backup location. Any time your personal files change, there will be a copy stored on a dedicated, external storage device of your choice. File History continuously protects your personal files stored in libraries (Documents, Music, Pictures, and Videos), as well as Desktop, Contacts, Favorites, and your OneDrive folders. File History doesn’t make a backup of your programs, settings, or operating system files. If you want to do full backup of your system, use the System Image backup utility. File History periodically (every hour by default) scans the file system for changes and copies changed files to another location. Over time, File History builds a complete history of the changes made to any personal file. When a specific point in time (PiT) version of a file or even an entire folder is needed, you can quickly find it and restore it. File History operates transparently and doesn’t affect the reliability or performance of Windows in any way. PC users are more mobile than ever. To address that, File History is optimized to better support laptops that constantly transition through power states, and are being connected and disconnected from networks and devices. There are two ways to configure File History, one using the classic Control Panel and another way is to use the modern File History option in the Settings app. If using the File History Settings app, click Start, type File History in the taskbar’s search box, and select File History Settings from the searched results. To access it from the old Control Panel, right-click Start, click on Control Panel in the menu, and select File History.Setting Up File History
Before you start using File History to back up your files, you’ll need to set up a drive to which you will save files. Microsoft recommends you use an external drive or network location to help protect your files against a crash or other PC problem. File History only saves copies of files in your libraries, contacts, favorites and on your desktop. If you have folders elsewhere you want backed up, you can add them to one of your existing libraries or create a new library. Connect the external hard drive to your computer. It can be any kind of storage with enough space, e.g., Hard Drive, Flash Drive, or Secure Digital Card (SD) card. Use the Windows Key + I to open the Settings app, and select Update & security > Backup (A). Under Back up using File History (B), click the + sign (C) beside Add a drive button. Windows 10 will search and fetch available drives (D). From the list, select the drive you want to use as the backup drive.Turn On File History
Once you select a drive for your backup, a toggle appears in the Back up using File History section to automatically backup your files. Turn it off to stop the File History feature. Click the More options link to get access to a number of options available in File History.Backup & Frequency
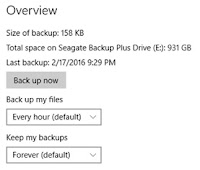
If you prefer to create an immediate backup, you can click the Back up now button. The two options underneath will give you the ability to configure frequency and the time you want to keep the backups. Under Back up my files, you can leave the Every hour (default) option, or you can click the drop-down list to select the frequency. Under Keep my backups, you can choose to keep File History backups Forever, Until space is needed, or a number of different time in months and years.Add & Remove Folders
You can add or remove folders that Windows 10 includes in your File History setup. To add a new folder, click the Add a folder (E) under Back up these folders section. To remove an existing folder from the backup routine, select it under Back up these folders section and click the Remove button (F). If you want to only backup a parent folder carrying child folders (that you don’t want to backup), specify those folders under Exclude these folders. Simply click the Add a folder (G) under this section, browse and select the location to exclude. Finally, if you want to stop using the drive to make backups or you’re planning to use a different drive, you can properly do so by clicking the Stop using drive button (H).Using a Network Location for File History Backup
Microsoft is improving the feature with Windows 10 for users to have more control using the Settings app. However, not every setting can be configured through the Settings app. For example, if you’re looking to set up a network location to make a File History automatic backup, you will need to use the classic Control Panel settings. To launch File History from the Control Panel, right-click the Start button and select Control Panel from the menu. Navigate through System and Security, and then go to File History. In the left pane, click Select drive (I). Click the Add network location link (J). Browse the network to locate the shared folder and click OK to add the location to the list. Click OK in control panel to confirm your configuration.NOTE: After backing up everything, Windows backs up only the changed files every hour. It keeps the original files, as well, giving you plenty of backups to choose from should you need them. Windows saves your backup in a folder named FileHistory on your chosen drive. Don’t move or delete that folder, or else Windows may not be able to find it again when you choose to restore it.






No comments:
Post a Comment